40 labelling of chloroplast
Chloroplast - Definition, Function and Structure | Biology Dictionary The word chloroplast comes from the Greek words khloros, meaning "green", and plastes, meaning "formed". It has a high concentration of chlorophyll, the molecule that captures light energy, and this gives many plants and algae a green color. Like the mitochondrion, the chloroplast is thought to have evolved from once free-living bacteria. Chloroplast Translation: Structural and Functional Organization ... Pulse labeling is the method of choice to directly measure translational activity in vivo. In this approach, isolated chloroplasts, cells, or intact plant tissues are fed with the 35 S-radiolabeled amino acids methionine and/or cysteine (Barkan, 1998). The isotopes are incorporated into newly synthesized proteins to an extent that mirrors their ...
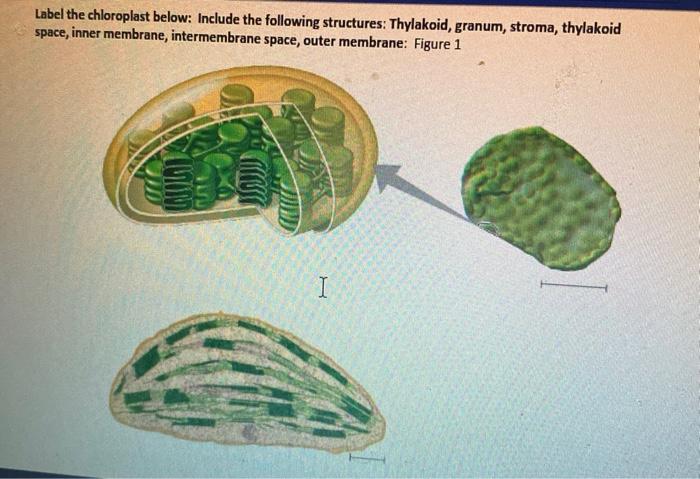
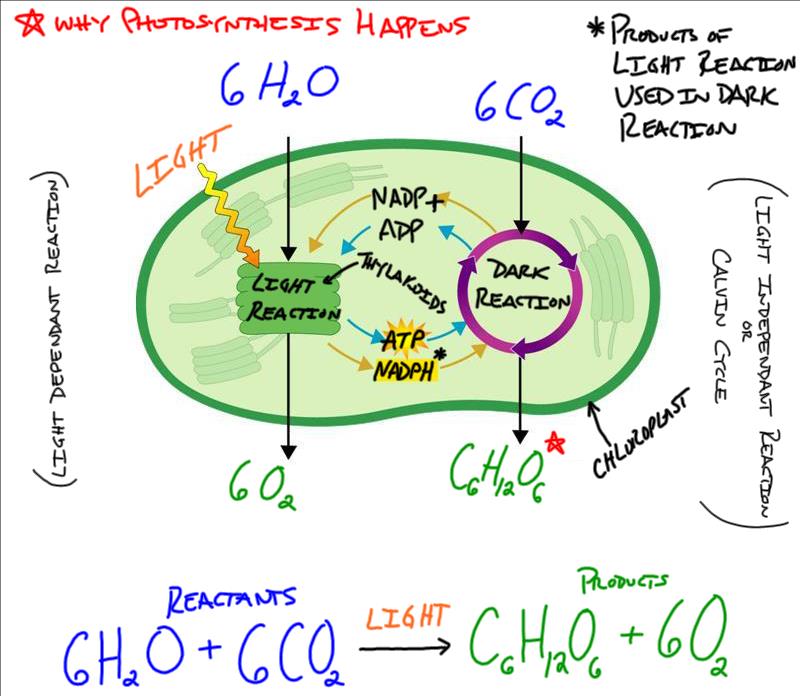
Labeling Chloroplast Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers A diagram of a chloroplast allows students to label the reactants, products, and locations of the light reaction and Calvin cycle during photosynthesis. Answer key included. A-Thom-ic Science. Subjects: Biology Grades: 7th - 10th Types: Worksheets Add to cart Wish List Chloroplast - drag-and-drop/labeling activities in Slides by

Labelling of chloroplast
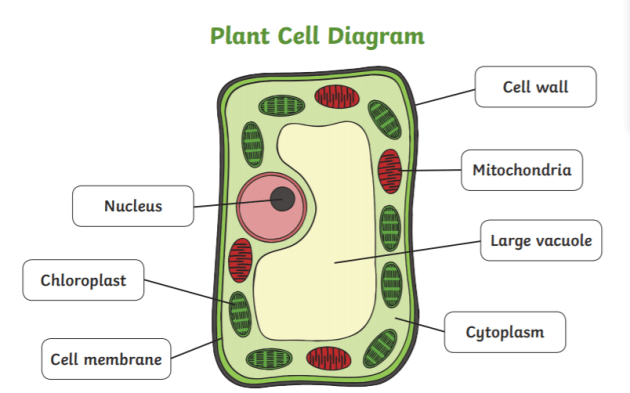
Plant cells - Cell structure - AQA - BBC Bitesize A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs. Plant cells also have additional structures: Function. Chloroplast. Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light ... Chloroplast - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The two-membrane chloroplast, observable under the microscope, is a key piece of evidence strengthening the theory that chloroplasts evolved when a eukaryotic cell captured a cyanobacteria and established Class Archaeplastida, the kingdom of plants. 4. The chloroplasts of non-Archaeplastida eukaryotes have three or four membrane layers. Labeling Chloroplast Diagram | Quizlet A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy. Where "light reactions" take place + 1 more side Term granum Definition stack of thylakoids + 1 more side Term lamella Definition tubes that connect the granum Location Term chloroplast DNA Definition
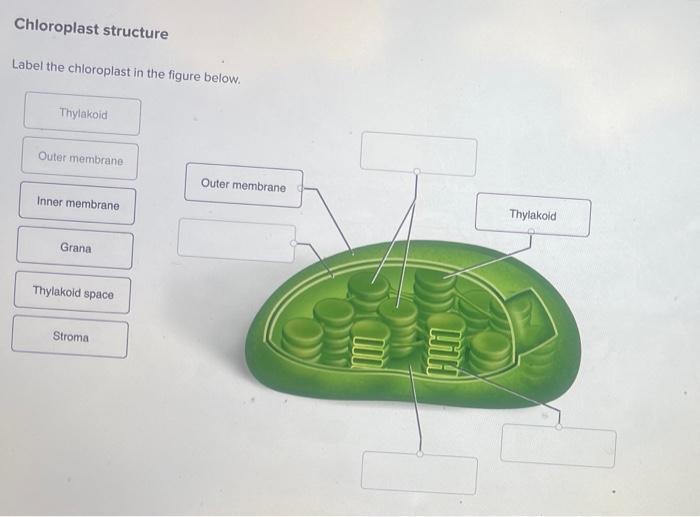
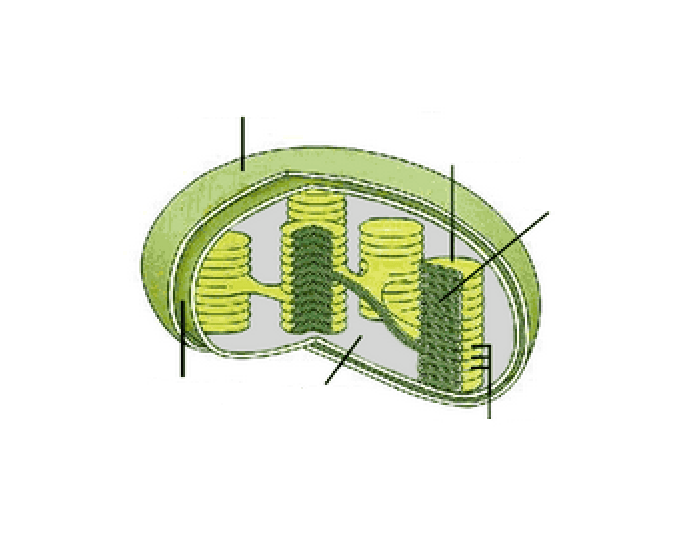
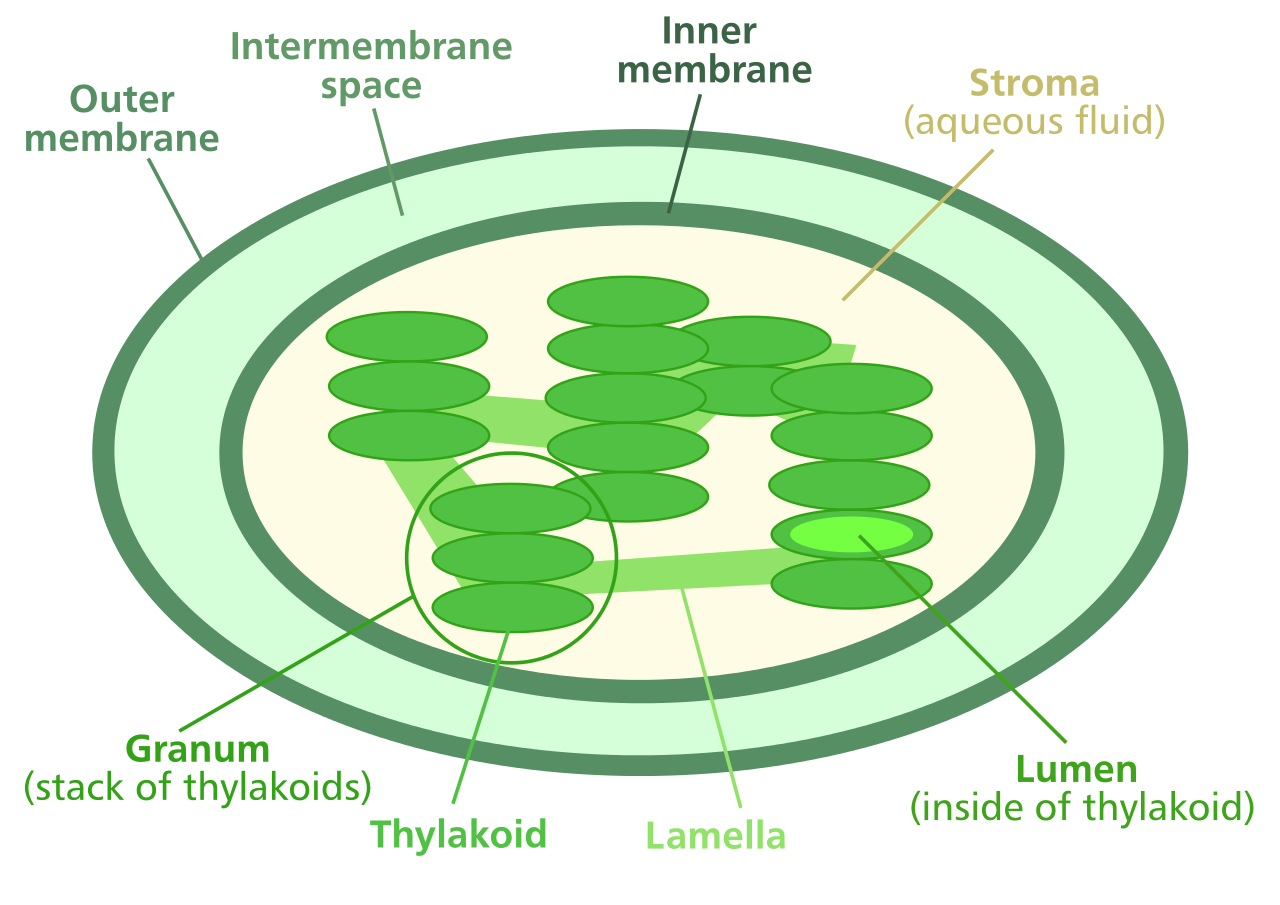
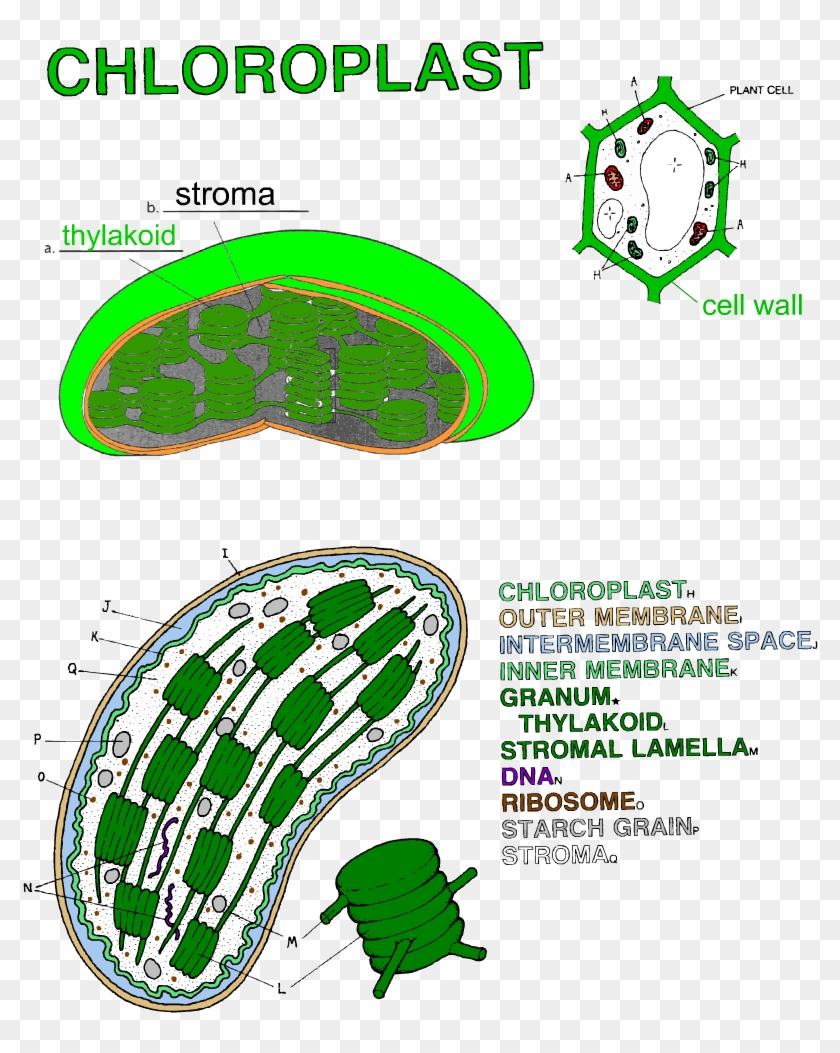
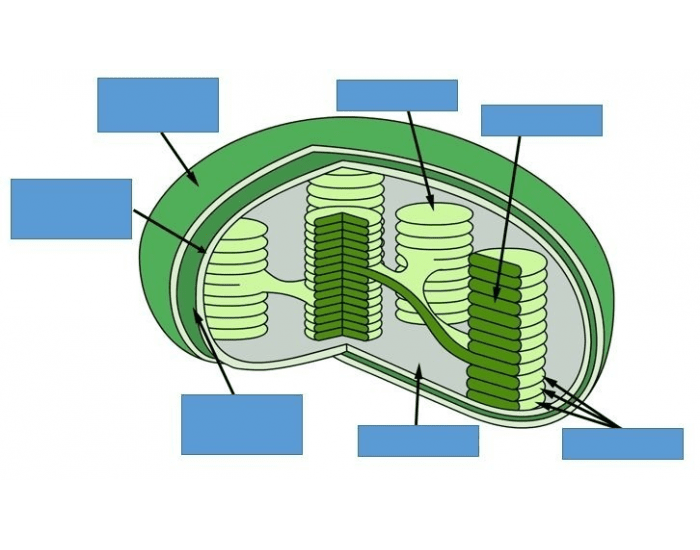
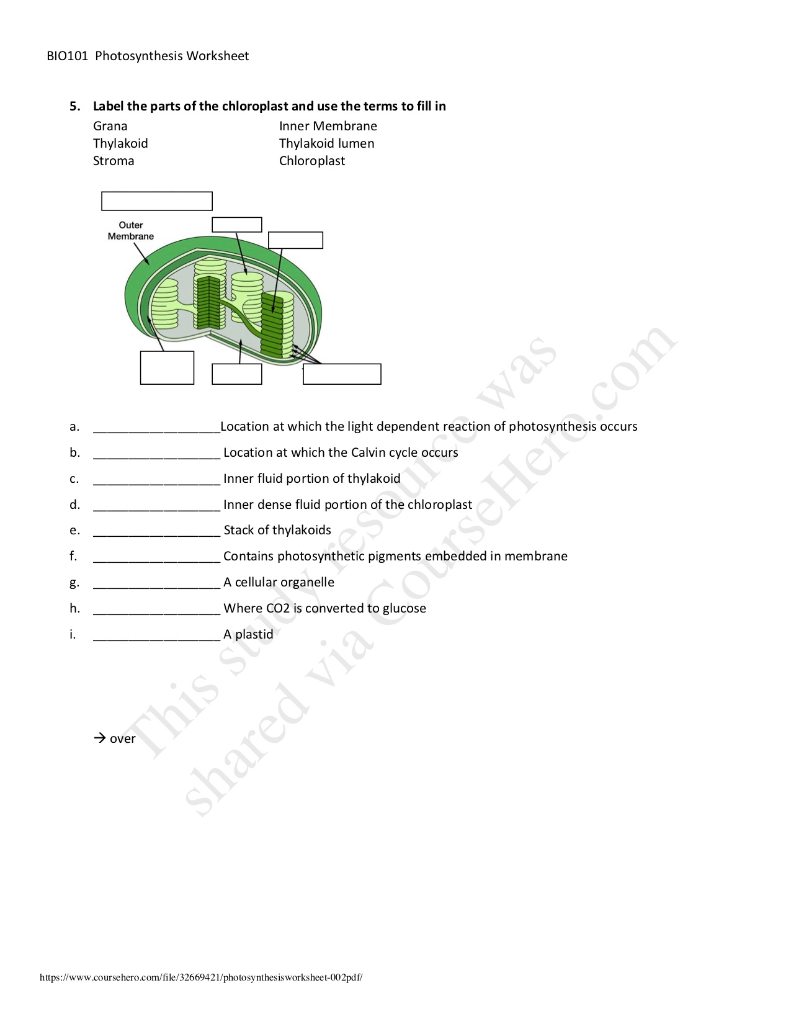
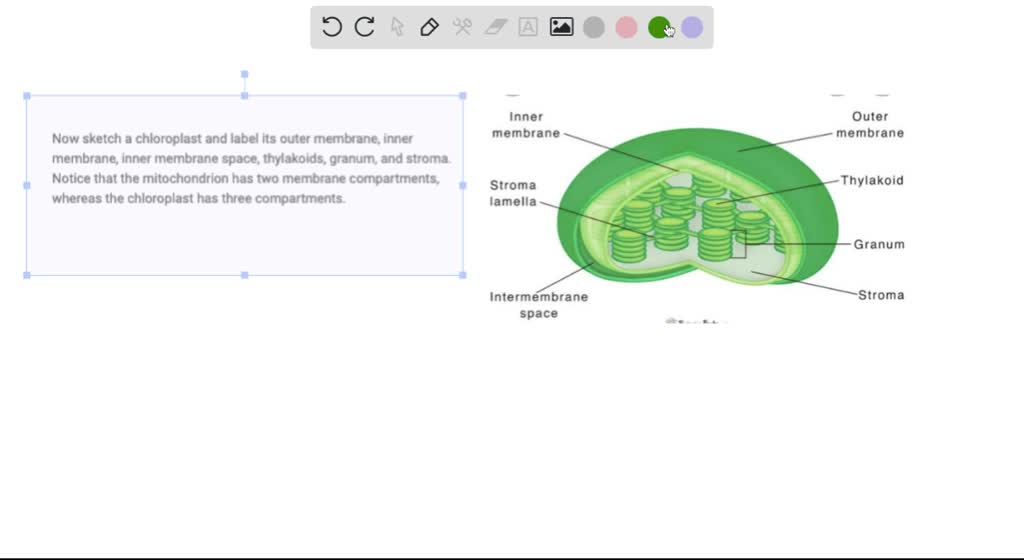
Labelling of chloroplast. Chloroplast Structure and Function - Coloring - The Biology Corner The Structure of the Chloroplast Chloroplasts are double membrane organelles with a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane that is folded into disc-shaped sacs called the thylakoid. Color and label the outer membrane light green . Color and label the inner membrane brown . Chloroplast: Diagram, Structure, Functions & More - Embibe Chloroplasts consist of Stroma, inner membrane, outer membrane, thylakoid membrane, and intermembrane space. Chloroplast Analogy An analogy for chloroplasts is that chloroplasts are like a kitchen of the cell. It is also known as the chef of the restaurant. Chloroplast Diagram how to draw chloroplast | how to draw chloroplast step by step | how to ... how to draw chloroplast | how to draw chloroplast step by step | how to draw and label a chloroplast 2,671 views Sep 19, 2019 55 Dislike Share AsapKNOWLEDGE 15.5K subscribers Hello Friends,... Chloroplast Label Teaching Resources | Teachers Pay Teachers This leaf and chloroplast diagram crossword is a great way to help review and reinforce the terminology associated with diagrams, especially those found in any anatomy or body systems unit. Subjects: Biology, General Science, Science Grades: 7th - 12th Types: Study Guides
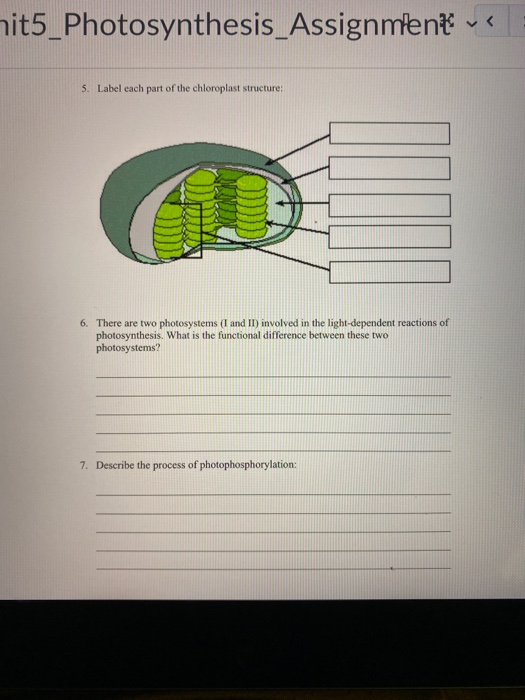
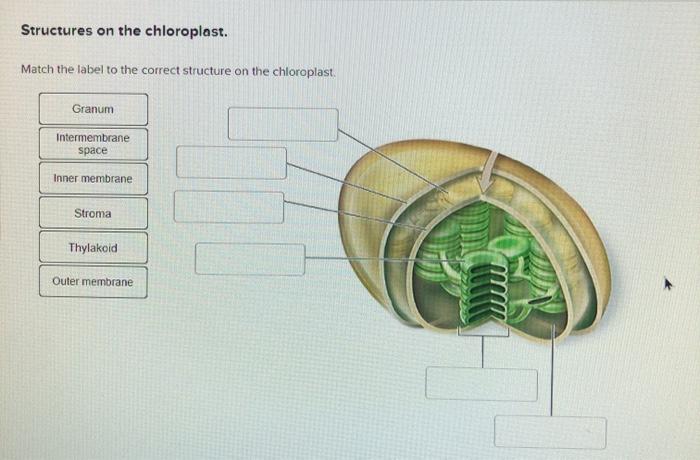
Chloroplast: Structure and Function - Biology Wise Chloroplasts are plastids that contain a network of membranes embedded into a liquid matrix, and harbor the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. It is this pigment that imparts a green color to plant parts, and serves to capture light energy. A detailed account of the structure and functions of chloroplasts has been provided below. Structure Chloroplasts- Definition, Structure, Functions and Diagram - Microbe Notes The word chloroplast is derived from the Greek words chloros, which means green, and plastes, which means "the one who forms". Chloroplasts are a type of membrane-bound plastids that contain a network of membranes embedded into a liquid matrix and harbor the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. Chloroplasts - Structure And Functions - A Level Biology The most important function of chloroplast is to make food by the process of photosynthesis. Food is prepared in the form of sugars. During the process of photosynthesis sugar and oxygen are made using light energy, water, and carbon dioxide. Light reactions takes place on the membranes of the thylakoids. BIOL Chapter 8 Review Flashcards | Quizlet Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which best represents the overall equation for photosynthesis?, Photosynthesis vs. respiration Place the statements in the appropriate pathway., Structures on the chloroplast. Match the label to the correct structure on the chloroplast. and more.
Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram Chloroplast contains chlorophyll and takes part in photosynthesis. The word chloroplast or chloroplastid has a Greek origin. Chloros means green, and plastos means molded. They can be found in plant cells ( Leaf anatomy) and some protists. They were first observed by Leeuwenhoek and N. Grew. Chloroplasts Structure & Characteristics Chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram Chloroplasts are a type of plastid—a round, oval, or disk-shaped body that is involved in the synthesis and storage of foodstuffs. Chloroplasts are distinguished from other types of plastids by their green colour, which results from the presence of two pigments, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b. Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast - BYJUS Chloroplasts- They are green coloured plastids, which comprise green-coloured pigments within the plant cell and are called chlorophyll. Leucoplasts- They are colourless plastids and are mainly used for the storage of starch, lipids and proteins within the plant cell. Table of Contents Definition Explanation Diagram Structure Function Chloroplast Function in Photosynthesis - ThoughtCo A chloroplast is a type of plant cell organelle known as a plastid. Plastids assist in storing and harvesting needed substances for energy production. A chloroplast contains a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis.
How to draw and label a chloroplast - YouTube How to draw and label a chloroplast Adimu Show 33.2K subscribers Subscribe 837 Share 65K views 4 years ago Cell Biology A beautiful drawing of a chloroplast . And it will teach you draw...
Labeling Chloroplast Diagram | Quizlet A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy. Where "light reactions" take place + 1 more side Term granum Definition stack of thylakoids + 1 more side Term lamella Definition tubes that connect the granum Location Term chloroplast DNA Definition
Chloroplast - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The two-membrane chloroplast, observable under the microscope, is a key piece of evidence strengthening the theory that chloroplasts evolved when a eukaryotic cell captured a cyanobacteria and established Class Archaeplastida, the kingdom of plants. 4. The chloroplasts of non-Archaeplastida eukaryotes have three or four membrane layers.
Plant cells - Cell structure - AQA - BBC Bitesize A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs. Plant cells also have additional structures: Function. Chloroplast. Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light ...





















Post a Comment for "40 labelling of chloroplast"