38 open-label study bias
Open label extension studies and patient selection biases An alternative method of analysis is proposed, which does not rely on the often unjustifiable assumption of outcomes being missing completely at random. Results: In an example open label extension study, with reported responder rate 43%, we show how an analysis allowing for patient selection biases produces a responder rate of just 28%. Transcatheter Mitral-Valve Repair in Patients with Heart ... Abstract Background Among patients with heart failure who have mitral regurgitation due to left ventricular dysfunction, the prognosis is poor. Transcatheter mitral-valve repair may improve their c...
What is an open label trial? | The BMJ May 23, 2014 · Researchers assessed the effectiveness of prazosin combined with scorpion antivenom in assisting recovery from scorpion sting. An open label randomised controlled trial study design was used. The control treatment was prazosin alone. The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India. Participants were patients with grade 2 scorpion envenomation, older than 6 months ...

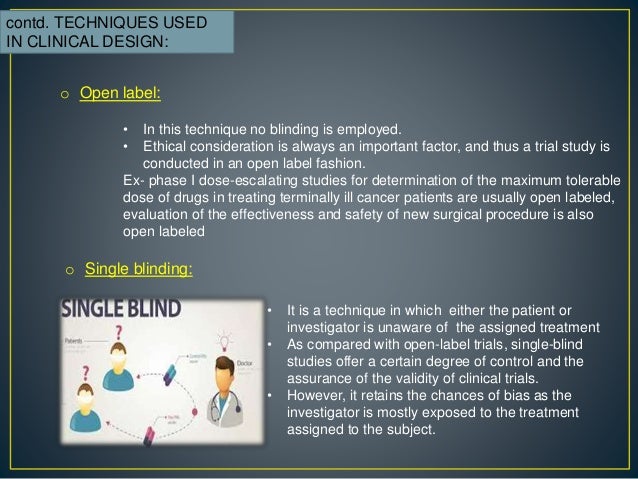
Open-label study bias
Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome assessment is ... Many trial designs do not permit blinding, and are therefore designed as open-label, with patients, clinicians, and other study investigators aware of treatment allocation. Research has suggested that these trials should use blinded outcome assessment to avoid bias in estimated treatment effects [ 6 - 10 ]. Open-label extension studies: do they provide meaningful ... - PubMed Random allocation into test and control groups is needed to produce precise incidence data on pharmacologically expected, or type A, adverse effects. Some increased confidence about incidence rates might result from the open-label extension study; however, as these studies are essentially uncontrolled and biased, the data are not of great value. Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics the difference of protective efficacy of ribavirin in humans and in hamsters may have several explanations: (1) the study in humans was not randomized and performed at posteriori, and grouping treated and nontreated patients may have introduced some bias; (2) the dose and mode of infection of niv used for the challenge or the virus replication in …
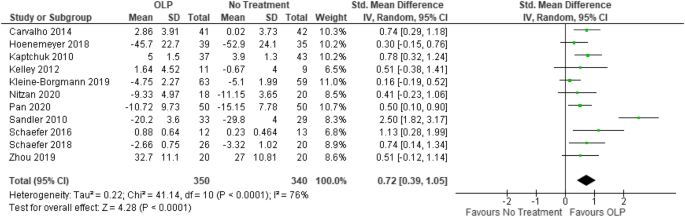
Open-label study bias. Consent to open label extension studies: some ethical issues A frequent feature of pharmaceutical research is the open label extension study, in which patients participating in double blind placebo controlled trials of new medications are invited, on completion of the initial trial, to take the study drug for some further period. Patients are openly given the active substance at this stage, regardless of their assignment in the initial trial. Transcatheter Mitral-Valve Repair in Patients with Heart Failure Nonetheless, potential bias cannot be completely ruled out. Second, the median follow-up was longer in the device group than in the control group, in part because of the lower mortality in the ... Open-label trial - Wikipedia Open-label trial From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia An open-label trial, or open trial, is a type of clinical trial in which information is not withheld from trial participants. In particular, both the researchers and participants know which treatment is being administered. Effects of open-label placebos in clinical trials: a ... - Nature Open-label placebos (OLPs) are placebos without deception in the sense that patients know that they are receiving a placebo. The objective of our study is to systematically review and analyze the...
At-home, sublingual ketamine telehealth is a safe and ... While this study demonstrates the promising potential of KAT for treating anxiety and depression and using telehealth for overcoming treatment access barriers and ensuring safety through remote monitoring, there are limitations of this study. The first is the drop in symptom survey completions at week 4 for around half of the records reviewed. What is an open label trial? | The BMJ 23/05/2014 · Researchers assessed the effectiveness of prazosin combined with scorpion antivenom in assisting recovery from scorpion sting. An open label randomised controlled trial study design was used. The control treatment was prazosin alone. The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India. Participants were patients with grade 2 scorpion … Effect of a 2-week interruption in methotrexate treatment ... Jun 27, 2022 · We did an open-label, prospective, two-arm, parallel-group, multicentre, randomised, controlled, superiority trial in 26 hospitals in the UK. We recruited adults from rheumatology and dermatology clinics who had been diagnosed with an immune-mediated inflammatory disease (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis with or without arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis, atopic dermatitis, polymyalgia ... Bias for Patient-Reported Outcomes in Open-Label Cancer Trials: How Big ... A common concern with patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in open-label trials is that a patient's knowledge of treatment received could influence their view and reporting of their symptoms. With this in mind, members of the US Food and Drug Administration explored the possibility of such bias in a recent viewpoint published in JAMA Oncology.
At-home, sublingual ketamine telehealth is a safe and effective ... While this study demonstrates the promising potential of KAT for treating anxiety and depression and using telehealth for overcoming treatment access barriers and ensuring safety through remote monitoring, there are limitations of this study. The first is the drop in symptom survey completions at week 4 for around half of the records reviewed. While sensitivity analyses … (PDF) What is an open label trial? - ResearchGate An open label randomised controlled trial study design was used. The control treatment was prazosin alone. The setting was a hospital and research centre in Mahad, a region of India. Participants... Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Open-label studies lack the rigor of blinded studies. Since the lack of blinding can introduce significant bias, reserve the use of open-label studies for situations in which blinding is neither feasible nor ethical or in cases where the outcome is completely objective, such as survival. Some situations include: • PDF Blinding Sponsors for Open Label Studies: Challenges and Solutions - MWSUG Even for open label studies, it's still desirable blind the study sponsor to reduce potential bias due to the sponsor knowing the treatment level aggregated data while the study is ongoing. The practice helps increase credibility of study results and thus should be followed, particularly for registration studies. In open label studies, in ...
Radiation doses and fractionation schedules in non-low-risk ductal ... 06/08/2022 · In patients with resected non-low-risk DCIS, a tumour bed boost after WBI reduced local recurrence with an increase in grade 2 or greater toxicity. The results provide the first randomised trial data to support the use of boost radiation after postoperative WBI in these patients to improve local control. The international scale of the study supports the …
External and internal validity of open label or double‐blind trials in ... Naturally, in open-label trials in anticoagulation there is a risk of a reporting bias of adverse events. Patients may research the new drug and its side-effects in publications and may be influenced in their reporting behaviour of potential side-effects. Furthermore, investigators may be equally susceptible to a reporting bias.
Survivorship bias - Wikipedia If sufficiently many scientists study a phenomenon, some will find statistically significant results by chance, and these are the experiments submitted for publication. Additionally, papers showing positive results may be more appealing to editors. This problem is known as positive results bias, a type of publication bias. To combat this, some ...
Exploring open-label bias in patient-reported outcome (PRO) emotional ... We compared PRO emotional domain results between investigational arms of paired open label and double-blind trials of the same drug and disease population. We hypothesized that greater improvement in emotional domain scores would be found in the investigational arms of open label compared to their paired blinded trials, providing evidence of bias.
Open-Label, Randomized, Multicenter, Phase III Study Comparing … 20/07/2022 · A phase III open-label study comparing oral paclitaxel plus E (oPac + E) 205 mg/m 2 paclitaxel plus 15 mg E methanesulfonate monohydrate 3 consecutive days per week versus IVpac 175 mg/m 2 once every 3 weeks was performed. Women with metastatic breast cancer and adequate organ function, at least 1 year from last taxane, were randomly assigned 2:1 to oPac …
Medical Cannabis for the Treatment of Dementia: A Review of ... Jul 17, 2019 · One open-label prospective cohort study included in the SR found that among 11 patients with Alzheimer’s disease, there was a statistically significant improvement in the overall NPI score from baseline following 28 days treatment with medical cannabis oil containing THC given orally at an initial dose of 2.5 mg twice daily and titrated up to ...
Investigating Potential Bias in Patient-Reported Outcomes in Open-label ... This Viewpoint highlights the importance of potential bias in patient-reported outcomes in open-label cancer trials and points to areas of research that could a. Our website uses cookies to enhance your experience. ... Kluetz PG. Investigating Potential Bias in Patient-Reported Outcomes in Open-label Cancer Trials. JAMA Oncol. 2019;5(4):457 ...
Medical Cannabis for the Treatment of Dementia: A Review of … 17/07/2019 · One open-label prospective cohort study included in the SR found that among 11 patients with Alzheimer’s disease, there were statistically significant improvements in the NPI subscales assessed from baseline following 28 days treatment with medical cannabis oil containing THC given orally at an initial dose of 2.5 mg twice daily and titrated up to 7.5 mg …
Login to your account - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 27/06/2022 · However, the study was at high risk of bias due to exclusion of participants after randomisation for previous SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease flare-up, a 33% dropout rate, and twice as many dropouts in the suspend methotrexate group than in the continue treatment group. CoronaVac elicits less immunity than mRNA-based and adenoviral platforms, and results …
What is an Open-Label Clinical Trial? - News-Medical.net Open-label trials are insufficient for providing data on these reactions. Open-label trials can increase the confidence about incidence rates, but as they are typically biased and uncontrolled,...
PDF RESEARCH ETHICS Consent to open label extension studies: some ethical ... of society. The situation I have in mind is the open label extension study, a relatively common type of drug trial. A recent MEDLINE search for "open label extension studies", limited by publication type to randomised controlled trials, produced 55 references between 1992 and 2000. Open label extension studies typically follow on from (and ...
PDF Clinical Trial Perspective - Open Access Journals which treatment each study participant is receiving; selection bias due to the investigator's attempt to guess the treatment assignment and selectively enroll study participants; and accidental bias due to impact of important unknown covariates on the primary out come. It is important to note that biases described in
Survivorship bias - Wikipedia Susan Mumm has described how survival bias leads historians to study organisations that are still in existence more than those that have closed. This means large, successful organisations such as the Women's Institute , which were well organised and still have accessible archives for historians to work from, are studied more than smaller charitable organisations, even though …
GRADE: Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, and Janssen COVID-19 … 29/10/2021 · In the open-label booster study, 4/344 (1.2%) participants experienced 5 SAEs during a median follow-up of 5.7 months after booster dose (administered at least 6 months after a 50 mcg (n=173) or 100 mcg (n=171) 2-dose primary series.) Data on an equivalent primary series comparison group was not available at the time of the GRADE assessment.
What is an open label trial? | The BMJ Open label trials are sometimes referred to as "non-masked" or "unblinded." If the trial is a non-pharmacological study, such as a trial of devices, or psychological and physical treatments, it may be referred to simply as "open." After recruitment to the trial, the participants were allocated to treatment using block randomisation.
Long-term efficacy and safety of moderate-intensity statin with ... 30/07/2022 · Our study has several limitations. First, this was an open-label trial. Physicians and the patients were aware of group assignment, which could potentially have led to bias in reporting patient symptoms. The nocebo effect of the statin therapy should be considered. However, an independent clinical endpoint committee masked to the therapy ...
A Meta-Analysis Comparing Open-Label versus Placebo-Controlled Clinical ... The present study is to provide whether open-label studies (OLS) may properly foresee the efficacy of randomized, placebo-controlled trials (RCTs) using OLSs and RCTs data for aripiprazole in the treatment of MDD, with the use of meta-analysis approach. ... The Egger test was also used for detection of publication bias to assess the bias ...
National Cancer Institute NCI's Dictionary of Cancer Terms provides easy-to-understand definitions for words and phrases related to cancer and medicine.
PDF What Are Open-Label Extension Studies For? - The Journal of Rheumatology factors. In the case of open-label extension studies, we feel that analysis of efficacy ought to regard treatment allocation as a possible explanatory variable (in addition to others, such as baseline status and time). The study by Mease and colleagues 1 reports the results of a 48-week open-label extension of a 24-week randomized
Radiation doses and fractionation schedules in non-low-risk ... Aug 06, 2022 · In patients with resected non-low-risk DCIS, a tumour bed boost after WBI reduced local recurrence with an increase in grade 2 or greater toxicity. The results provide the first randomised trial data to support the use of boost radiation after postoperative WBI in these patients to improve local control. The international scale of the study supports the generalisability of the results.
Open label extension studies: research or marketing? | The BMJ Open label extension studies allow continued prescribing of unlicensed drugs after a randomised trial, but it is unclear whether patients or drug companies are benefiting the most Properly designed and conducted open label extension studies can provide rigorous information on long term safety and tolerability of potential new drugs. This in turn can benefit the licensing application for the ...
National Center for Biotechnology Information National Center for Biotechnology Information
Some Blinding Techniques in Clinical Trials - Blogger The firewall between the sponsor the investigator/clinical research organization can also be implemented in an open label study or single-blind study so that the sponsor is prevented to access the cumulative data for the primary efficacy endpoint for analysis. ... Brennan C Kahan (2014) Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome ...
Open label extension studies and patient selection biases Due to the inherent limitations of open-label extension studies (including open-label design creating potential bias, completer populations possibly representing only responders to therapy, and...
Open-Label Extension Studies | SpringerLink The number of open-label extension studies being performed has increased enormously in recent years. Often it is difficult to differentiate between these extension studies and the double-blind, controlled studies that preceded them. If undertaken primarily to gather more patient-years of exposure to the new drug in order to understand and gain confidence in its safety profile, open-label ...
External and internal validity of open label or double-blind trials in ... Risk of bias in internal validity in open-label and double-blind trials Internal validity of a clinical trial is influenced by a number of factorsintroducingapotentialforbias,includingselectionbias, subject retention performance bias, detection bias and attrition bias [6]. Patient selection bias
Understanding Clinical Trial Terminology: What is an Open Label ... Clinical trials are a key part of evaluating investigational treatments. People who volunteer to participate in clinical trials, along with investigators and study coordinators, are all key to a trial's success. Often, clinical trials use a double-blind approach: study participants and researchers don't know which treatment the patient is receiving. Alternatively, sometimes, trials are ...
Open-Label Trial - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics the difference of protective efficacy of ribavirin in humans and in hamsters may have several explanations: (1) the study in humans was not randomized and performed at posteriori, and grouping treated and nontreated patients may have introduced some bias; (2) the dose and mode of infection of niv used for the challenge or the virus replication in …
Open-label extension studies: do they provide meaningful ... - PubMed Random allocation into test and control groups is needed to produce precise incidence data on pharmacologically expected, or type A, adverse effects. Some increased confidence about incidence rates might result from the open-label extension study; however, as these studies are essentially uncontrolled and biased, the data are not of great value.
Reducing bias in open-label trials where blinded outcome assessment is ... Many trial designs do not permit blinding, and are therefore designed as open-label, with patients, clinicians, and other study investigators aware of treatment allocation. Research has suggested that these trials should use blinded outcome assessment to avoid bias in estimated treatment effects [ 6 - 10 ].









![PDF] The Clinical Viewpoint: Definitions, Limitations of ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/0d341492d445073e64d1ccb6985e4ad763a3d1f7/2-Table1-1.png)




![PDF] Bias was reduced in an open-label trial through the ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/814ad6ccbfa9defca4d2b00c4672f9070cf6b8da/16-Figure1-1.png)





![PDF] Safety of oral ivermectin during pregnancy: a systematic ...](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/4e1f7ccf234e029667ee9c730262ec03978ba2bd/5-Table3-1.png)



Post a Comment for "38 open-label study bias"